Cancer Screening
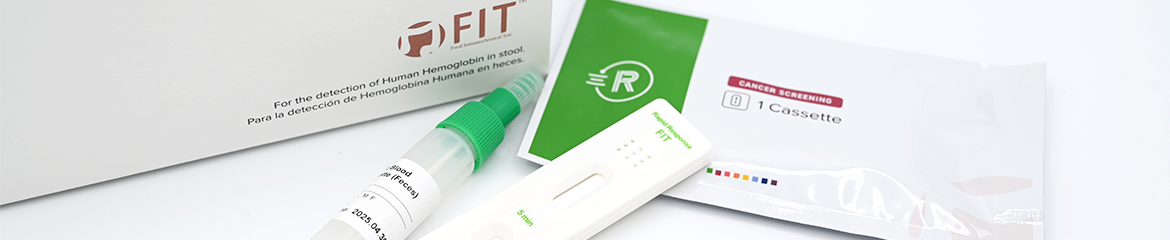
The Rapid Response® Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) is an immunochromatographic assay intended for the determination of human hemoglobin in feces by professional laboratories or physician’s offices. It is useful to determine gastrointestinal bleeding found in a number of gastrointestinal disorders such as colorectal carcinoma, colon polyps, diverticulitis and ulcerative colitis.

Format: Cassette
Kit Size: 2 Tests/Kit
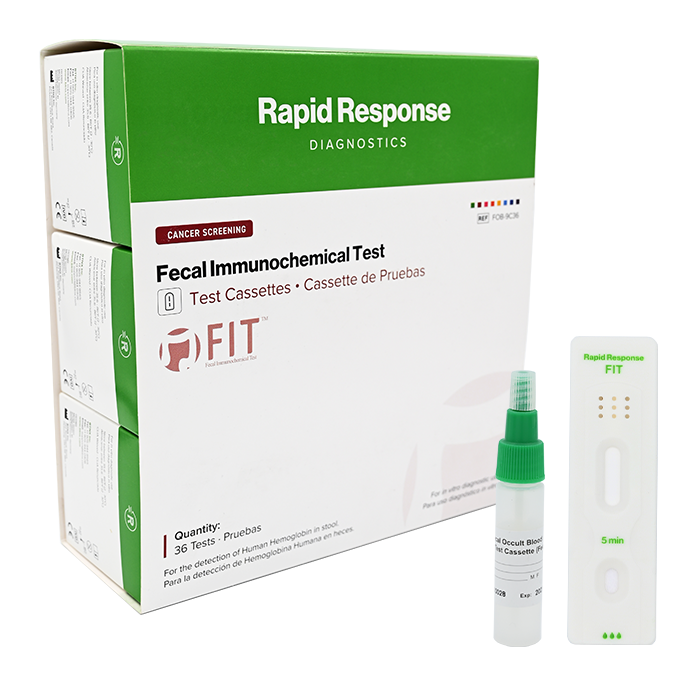
Format: Cassette
Kit Size: 36 Tests / Kit

Format: Papers
Kit Size: 50 Mailers / Kit
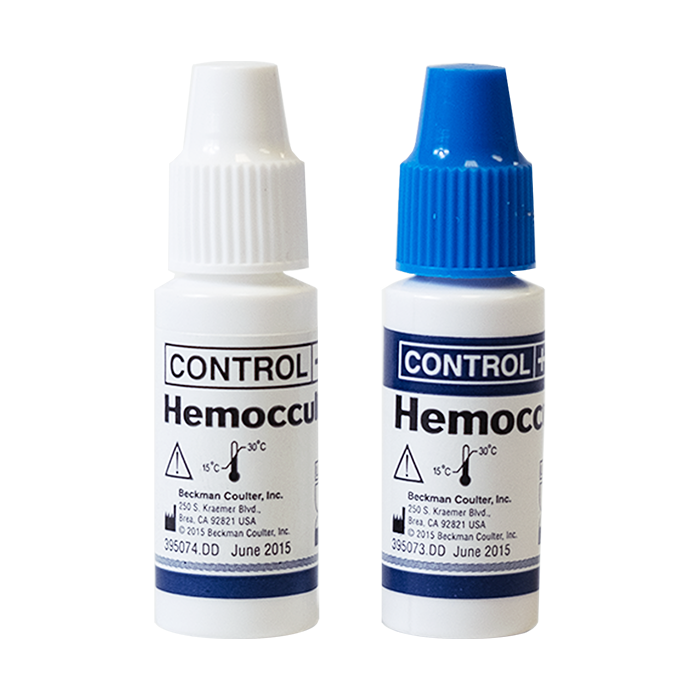
Kit Size: 1 Pair / Kit
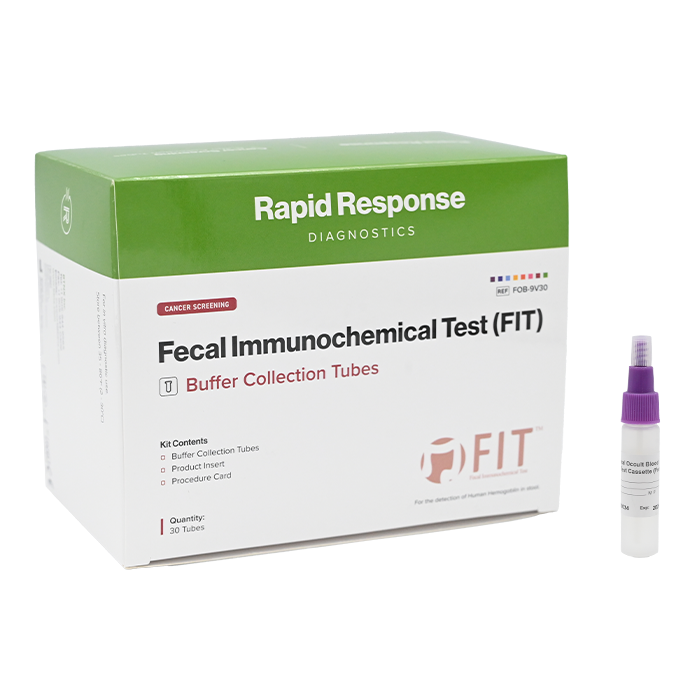
Kit Size: 30 Tubes / Kit
Introduction to Cancer Screening
What is colorectal cancer?
Colorectal cancer is a disease in which cells in the colon or rectum grow out of control. Abnormal growths, called polyps, form in the colon or rectum. Over time, some polyps may turn into cancer. Screening tests aid in the early detection of colorectal cancer, providing information for when to seek treatment.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of colorectal cancer include:
- Change in bowl habits.
- Blood in or on your stool (bowel movement).
- Diarrhea, constipation, or feeling that the bowel does not empty all the way.
- Abdominal pain, aches, or cramps that don’t go away.
- Unknown weight loss
Source: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Division of Cancer Prevention and Control
What are the risk factors?
The risk of colorectal cancer increases as you get older. Risk factors include:
• Inflammatory bowel disease
• Family history of colorectal cancer
• Genetic syndrome
• Lack of physical exercise
• Diet that is low in fruit and vegetables
• Low fiber and high fat diet
• Diet that is high in processed meats
• Overweight and obesity
• Alcohol consumption
• Smoking or tobacco use
What can I do to reduce my risk?
The most effective way to reduce your risk of colorectal cancer is to get screened early. The American Cancer Society recommends regular colorectal cancer screening starting at age 45 for people at average risk.
What should I know about screening?
A screening test is used to detect a disease in individuals who do not show any symptoms. A screening test can detect precancerous polyps, allowing for early treatment and removal of these precancerous growths before they turn into cancer.
What are the test options for colorectal cancer screening?
Colorectal cancer screening is crucial for early detection and treatment. There are two main groups for colorectal cancer screening tests:
- Stool-based tests – these tests look at the stool (feces) for possible signs of colorectal cancer or polyps. There are over-the-counter tests that can be done at home, which makes it easier and convenient for regular screening. These tests are less invasive but need to be done regularly. However, if the result from these tests is positive (abnormal), a colonoscopy is needed to confirm if you have cancer.
- Tests include guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT), Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT), FIT-DNA test
- Visual (structural) exams – these tests look at the inside of the colon and rectum for abnormal areas that may be cancer or polyps. These tests are done less often than stool-based tests but require pre-testing preparation.
- Tests include Colonoscopy, CT colonography, sigmoidoscopy
Source: Colorectal Cancer Screening Tests | Sigmoidoscopy & Colonoscopy | American Cancer Society
Rapid Response Tests
| Product | Details | Benefits |
| Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Cassette | Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Cassette contains 3 boxes with 12 individually packed test cassettes, 12 specimen collection tubes with extraction buffer. Total of 36 tests per kit. |
|
| Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Mailers | Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Mailers are complimentary paper kits that are used with the Rapid Response™ Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Cassette for at-home stool collection. This kit offers enhanced convenience and is a user-friendly option, designed for a mess-free and simplified collection process. Contains 50 mailers/kit. |
|
| Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Control Solutions | Rapid Response Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Control Solutions are used with the Rapid Response™ Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) Cassette. Contains 1 pair/kit (1 positive and 1 negative control vials). |
|
How do FIT tests work?
FIT screening tests look for occult (hidden) blood in stool and help detect early signs of cancerous or pre-cancerous growths in the colon. Regular screening and treatment can help reduce risks of serious adverse effects of colorectal cancer on a person’s overall health.
About the Results and Interpreting Results
- Positive: Two red lines appear. One red line should be in the control region I and another red line should be in the test line region (T).
- Negative: One red line appears in the control line region I. No line appears in the test line region (T).
- Invalid: If no lines appear or if the control line doesn’t appear, the test results are not valid. Retesting should be performed.
Consult with your healthcare provider for follow-up and advice.
Find the best solution for your needs
Our sales representatives can help set you up for success! Contact our team today!
Polyps are mushroom-like growths that form when cells lining the colon grow abnormally. They can become cancerous over time.
According to the WHO, colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the United States.
According to the Canadian Cancer Society, colorectal cancer is the 4th most common cancer in Canada.
See your doctor for yearly screenings if you are aged 45 or older. The American Cancer Society recommends to consider starting to screen at age 45.
Guaiac-based Fecal Occult Blood Test (gFOBT) – This test detects occult (hidden) blood in the stool through a chemical reaction. It is done once a year. Stool sample is collected and then return the kit to the doctor or lab. Food and medication can affect the results of this test.
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) – This test is an effective tool for colorectal cancer screening and for symptomatic assessments. This test detects occult (hidden) blood in the stool by using antibodies. It is done once a year. The test can be visually interpreted. These tests have greater clinical and analytical sensitivity.1,2 Unlike guaiac-based FOB tests (gFOBT), they have no dietary or medication restrictions prior to testing.
- Fraser CG et al. Newer Fecal Tests: Opportunities for Professionals in Laboratory Medicine. Clin Chem. 2012;58(6):963−5.
- Halloran, SP et al. European guidelines for quality assurance in colorectal cancer screening and diagnosis. First Edition. Faecal occult blood testing. Endoscopy. 2012;44:1−23.
Talk to your healthcare provider to discuss if you are eligible for a FIT test.
It is recommended that people at average risk get screened with the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every 2 years. (Cancer Care Ontario)
The American Cancer Society recommends regular screening starting at age 45. It is recommended to take a FIT test every year.
Which test to use depends on your preferences, medical condition, personal or family history, genetic syndrome, and available resources. Talk to your doctor about which test to use. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)

 Canada
Canada